TRANSMISSION MEDIUM
Discussion on: Bit Rate and Baud Rate,
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN BIT RATE AND BAUD RATE
| Bit rate is transmission of number of bits per second. It can be defined as per second travel number of bits. | Baud rate is number of signal units per second. It can be defined as per second number of changes. |
|---|---|
| Bit rate focusses on computer efficiency. | Baud rate focusses on data transmission. |
| Bit Rate = Baud rate x the number of bit per baud | Baud Rate = Bit rate / the number of bit per baud |
| The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second unit (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction with an SI prefix such as kilo (1 kbit/s = 1,000 bit/s), mega (1 Mbit/s = 1,000 kbit/s), giga (1 Gbit/s = 1,000 Mbit/s) or tera (1 Tbit/s = 1,000 Gbit/s).[2] The non-standard abbreviation bps is often used to replace the standard symbol bit/s, so that, for example, 1 Mbps is used to mean one million bits per second. | The baud rate is the rate at which information is transferred in a communication channel. Baud rate is commonly used when discussing electronics that use serial communication. In the serial port context, "9600 baud" means that the serial port is capable of transferring a maximum of 9600 bits per second. |
end...
TRANSMISSION MEDIUM
* In data communication terminology, a transmission medium is a physical
path between the transmitter and the receiver i.e it is the channel
through which data is sent from one place to another.
* The medium through which the signal transfer from the sender to the receiver is known as transmission medium.
* Transmission Media is broadly classified into the following types:
1. Guided Media:
- High Speed
- Secure
- Used for comparatively shorter distances
There are 3 major types of Guided Media:
(i) Twisted Pair Cable –
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP):
This type of cable has the ability to block interference and does not depend on a physical shield for this purpose. It is used for telephonic applications.Advantages:
- Least expensive
- Easy to install
- High-speed capacity
- Susceptible to external interference
- Lower capacity and performance in comparison to STP
- Short distance transmission due to attenuation
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP):
This type of cable consists of a special jacket to block external interference. It is used in fast-data-rate Ethernet and in voice and data channels of telephone lines.Advantages:
- Better performance at a higher data rate in comparison to UTP
- Eliminates crosstalk
- Comparatively faster
- Comparatively difficult to install and manufacture
- More expensive
- Bulky

Twisted Pair 
RJ45
(ii) Coaxial Cable –
It carries the signal in higher frequency ranges than the twisted pair cable. The co-axial cable is standardized by RG rating. The RG standard specified the physical specification of the cable. The popular categories are RG-59(cable TV) and RG-58(Ethernet LAN). It has an outer plastic covering containing 2 parallel conductors each having a separate insulated protection cover. The coaxial cable transmits information in two modes: Baseband mode(dedicated cable bandwidth) and Broadband mode(cable bandwidth is split into separate ranges). Cable TVs and analog television networks widely use Coaxial cables.
Advantages:
- High Bandwidth
- Better noise Immunity
- Easy to install and expand
- Inexpensive
Disadvantages:
- Single cable failure can disrupt the entire network
- Although the co-axial cable has a much higher bandwidth, The signal weak rapidly and need frequent use of repeater.
 |
| Co-axial cable |
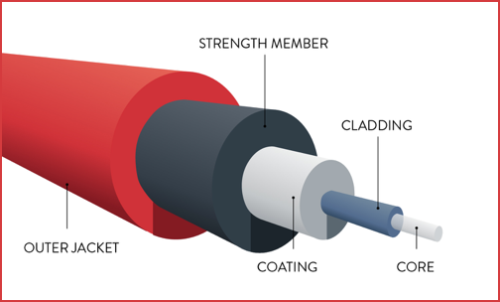
(iii) Optical Fibre Cable –
A fiber optic cable is made of glass or plastic and transmit signal in the form of light.
It uses the concept of reflection of light through a core made up of glass. The core is surrounded by a less dense glass covering called the cladding. It is used for the transmission of large volumes of data.
At the center is the glass core through which light can propagate. The core is surrounded by the glass cladding with the lower index of reflection than the core to keep all the light inside the core. A thin plastic jacket is used to protect the cladding.
The current technology support two nodes for propagation of light along optical channel each require fiber with different character i> Multi mode, ii> Single mode.
The cable can be unidirectional or bidirectional. The WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer) supports two modes, namely unidirectional and bidirectional mode.
Advantages:
- Increased capacity and bandwidth
- Lightweight
- Less signal attenuation
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference
- Resistance to corrosive materials
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to install and maintain
- High cost
- Fragile
Multi Mode:
Since any light ray incident on the boundary above the critical angle will be reflected internally. So it is possible to have many different rays bouncing around at different angle, each ray is said to have a different mode. A fiber having this property is known as multi mode fiber.
Single Mode:
If the fiber diameter is reduced to a few wave length at light the fiber act as web guide and the light can be propagates only a straight line without any bouncing. This is known as single mode in which one signal can travel.
(iv) Stripline
Stripline is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium invented by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Force Cambridge Research Centre in the 1950s. Stripline is the earliest form of the planar transmission line. It uses a conducting material to transmit high-frequency waves it is also called a waveguide. This conducting material is sandwiched between two layers of the ground plane which are usually shorted to provide EMI immunity.
(v) Microstripline
In this, the conducting material is separated from the ground plane by a layer of dielectric.
2. Unguided Media:
It
is also referred to as Wireless or Unbounded transmission media.No
physical medium is required for the transmission of electromagnetic
signals.
Features:
- The signal is broadcasted through air
- Less Secure
- Used for larger distances
There are 3 types of Signals transmitted through unguided media:
(i) Radiowaves –
These
are easy to generate and can penetrate through buildings. The sending
and receiving antennas need not be aligned. Frequency Range:3KHz – 1GHz.
AM and FM radios and cordless phones use Radiowaves for transmission.
Further Categorized as (i) Terrestrial and (ii) Satellite.
(ii) Microwaves –
It
is a line of sight transmission i.e. the sending and receiving antennas
need to be properly aligned with each other. The distance covered by
the signal is directly proportional to the height of the antenna.
Frequency Range:1GHz – 300GHz. These are majorly used for mobile phone
communication and television distribution.
Infrared waves are used for very short distance communication. They cannot penetrate through obstacles. This prevents interference between systems. Frequency Range:300GHz – 400THz. It is used in TV remotes, wireless mouse, keyboard, printer, etc.


Comments
Post a Comment