ANALOG AND DIGITAL NOTES
Discussion on, DIGITAL AND ANALOG DATA, FDM
COMPARE BETWEEN DIGITAL AND ANALOG DATA
| DIGITAL DATA | ANALOG DATA |
|---|---|
| Digital data refers to information which is discrete. | Analog data refers to information which is continuous. |
| Example: A digital clock that reports the hours and the minutes will change suddenly from 10:10 to 10:11. | Example: An analog clock that has hour, minute, and second hands are continuous. |
| Digital data take on discrete values. Data are stored in computer memory in the form of 0's and 1's. They can be converted to a digital signal or modulated into an analog signal for transmission across a medium. | Analog data such as sound take on continuous values. When someone speaks, an analog wave is created in air. This can be captured by a microphone and converted to an analog signal and this analog signal is then converted to digital signal. |
end...
WHAT IS MODULATION ?
* Modulation is the process of converting data into electrical signals optimized for transmission.
* Modulation techniques are roughly divided into four types: Analog modulation, Digital modulation, Pulse modulation , and Spread spectrum method.
* Modulation is
simply a widely used process in communication systems in which a very
high-frequency carrier wave is used to transmit the low-frequency
message signal so that the transmitted signal continues to have all the
information contained in the original message signal.
* Modulation is the process of influencing data information on the carrier, while demodulation is the recovery of original information at the distant end from the carrier. A modem is an equipment that performs both modulation and demodulation.
* In analog modulation an analog modulation signal is impressed on the carrier. Examples are amplitude modulation (AM) in which the amplitude (strength) of the carrier wave is varied by the modulation signal, and frequency modulation (FM) in which the frequency of the carrier wave is varied by the modulation signal.
* There are many digital modulation techniques the most famous are ASK, FSK, PSK and QAM
end...
COMPARE BETWEEN ASK, FSK AND PSK
| ASK | FSK | PSK |
|---|---|---|
| Full form is Amplitude-shift keying. | Full form is Frequency-shift keying. | Full form is Phase-shift keying. |
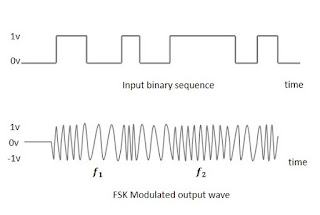
| ASK is a type of Amplitude Modulation which represents the binary data in the form of variations in the amplitude of a signal. | FSK is the digital modulation technique in which the frequency of the carrier signal varies according to the digital signal changes. FSK is a scheme of frequency modulation. | PSK is the digital modulation technique in which the phase of the carrier signal is changed by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a particular time. |
| The ASK technique is also commonly used to transmit digital data over optical fiber. For LED transmitters, binary 1 is represented by a short pulse of light and binary 0 by the absence of light. The simplest and most common form of ASK operates as a switch, using the presence of a carrier wave to indicate a binary one and its absence to indicate a binary zero. This type of modulation is called on-off keying (OOK), and is used at radio frequencies to transmit Morse code. | The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands. | PSK technique is widely used for wireless LANs, bio-metric, contactless operations, along with RFID and Bluetooth communications. |
| No further divided. | The simplest FSK is binary FSK (BFSK). BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary (0s and 1s) information. Many variations are there, like 2.1 Continuous-phase frequency-shift keying, 2.2 Gaussian frequency-shift keying, 2.3 Minimum-shift keying | PSK is of two types, depending upon the phases the signal gets shifted. They are Binary phase-shift keying(BPSK), Quadrature phase-shift keying(Qpsk). |
| . |
.p |
end...
WHAT IS FDM?
- In FDM, signals to be transmitted must be analog signals. Thus digital signals need to be converted to analog form, if they are to use FDM.
- FDM requires that the bandwidth of a link should be greater than the combined bandwidths of the various signals to be transmitted. Thus each signal having different frequency forms a particular logical channel on the link and follows this channel only.
- Channels are then separated by the strips of unused bandwidth called guard bands. These guard bands prevent the signals from overlapping.
ADVANTAGES OF FDM:
- A large number of signals (channels) can be transmitted simultaneously.
- FDM does not need synchronization between its transmitter and receiver for proper operation.
- Demodulation of FDM is easy.
- Due to slow narrow band fading only a single channel gets affected.
DISADVANTAGES OF FDM:
- The communication channel must have a very large bandwidth
- Intermodulation distortion takes place.
- Large number of modulators and filters are required.
- FDM suffers from the problem of crosstalk.
- ll the FDM channels get affected due to wideband fading.
APPLICATIONS OF FDM
- FDM is used for FM & AM radio broadcasting. Each AM and FM radio station uses a different carrier frequency. In AM broadcasting, these frequencies use a special band from 530 to 1700 KHz. All these signals/frequencies are multiplexed and are transmitted in air. A receiver receives all these signals but tunes only one which is required. Similarly FM broadcasting uses a bandwidth of 88 to 108 MHz.
- FDM is used in television broadcasting.
- First generation cellular telephone also uses FDM
end...
end...





Comments
Post a Comment